Understanding PCB Assembly Meaning
Winnie King
In today’s technology-driven world, nearly every electronic device relies on a printed circuit board (PCB) to function. From smartphones and laptops to medical devices and automotive systems, PCBs are the backbone of modern electronics. But what exactly is pcb assembly meaning? This term goes beyond just attaching components to a board—it represents a sophisticated, multi-step process that transforms a bare circuit board into a fully functional electronic unit.
This article dives deep into the pcb assembly meaning, explaining its significance, methods, applications, and why understanding this process is essential for engineers, designers, and businesses involved in electronics development.
What Does PCB Assembly Mean?
At its core, the pcb assembly meaning refers to the process of mounting and soldering electronic components onto a printed circuit board to create a working electronic assembly—commonly known as a PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly). Unlike a bare PCB, which contains only copper traces and pads, a completed PCB assembly includes resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), connectors, and other active or passive parts necessary for operation.
The transformation from a blank board to a functioning system involves precision engineering, advanced machinery, and rigorous quality control. The result? A compact, reliable platform capable of processing signals, managing power, and enabling communication between various subsystems within an electronic product.
Understanding the pcb assembly meaning is not just about knowing the technical steps—it's about appreciating how this process enables innovation across industries such as telecommunications, healthcare, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
Key Steps in the PCB Assembly Process
To fully grasp the pcb assembly meaning, it's important to understand the typical stages involved in assembling a PCB. While variations exist depending on design complexity and production volume, most assemblies follow a standardized sequence:
1. Solder Paste Application
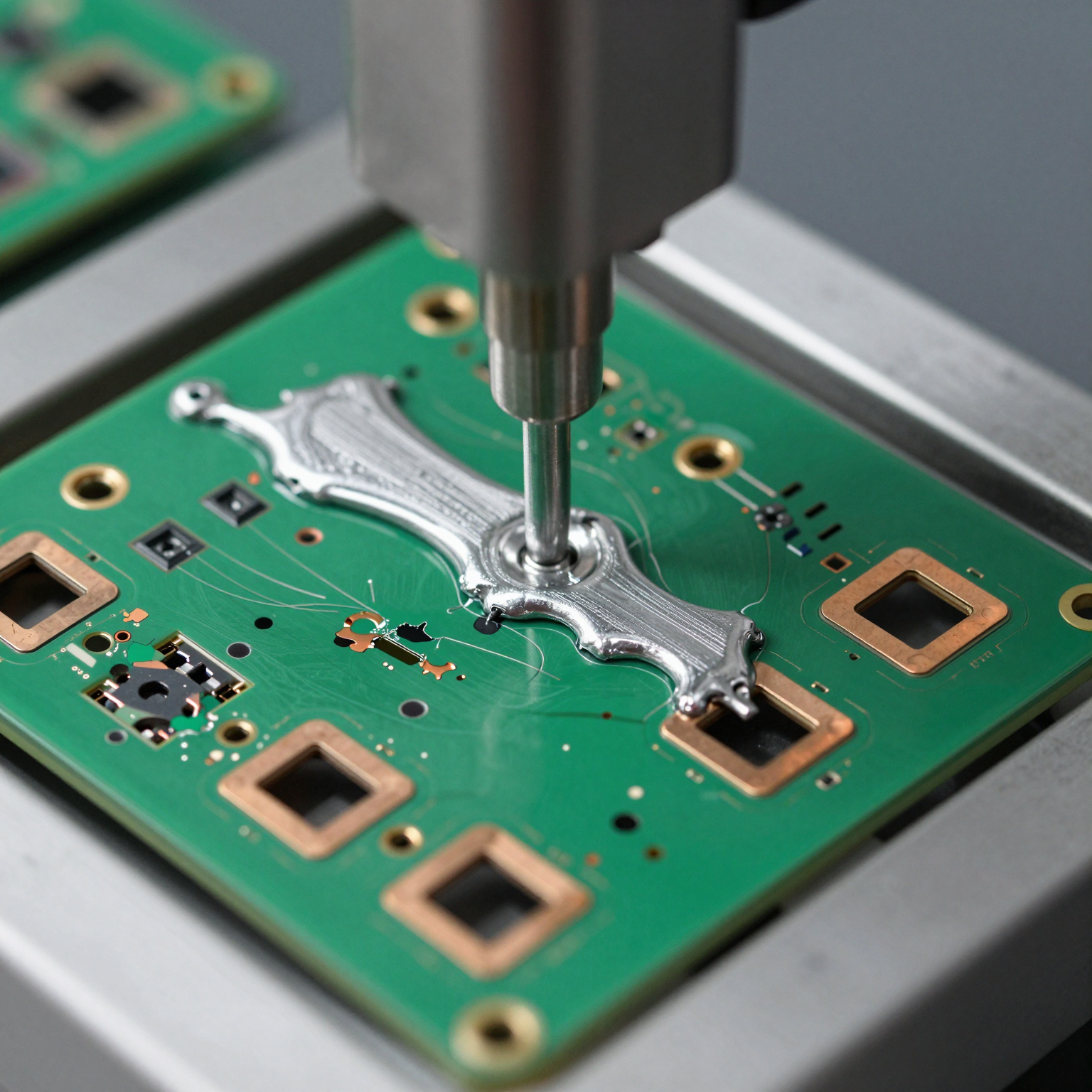
The first step involves applying solder paste to the surface of the PCB using a stencil. This paste, made of tiny solder particles suspended in flux, is precisely deposited only on the pads where surface-mount components will be placed.
2. Component Placement

Using high-speed pick-and-place machines, electronic components are accurately positioned on the solder paste-coated pads. These machines can place thousands of components per hour with micron-level accuracy, ensuring reliability and consistency.
3. Reflow Soldering
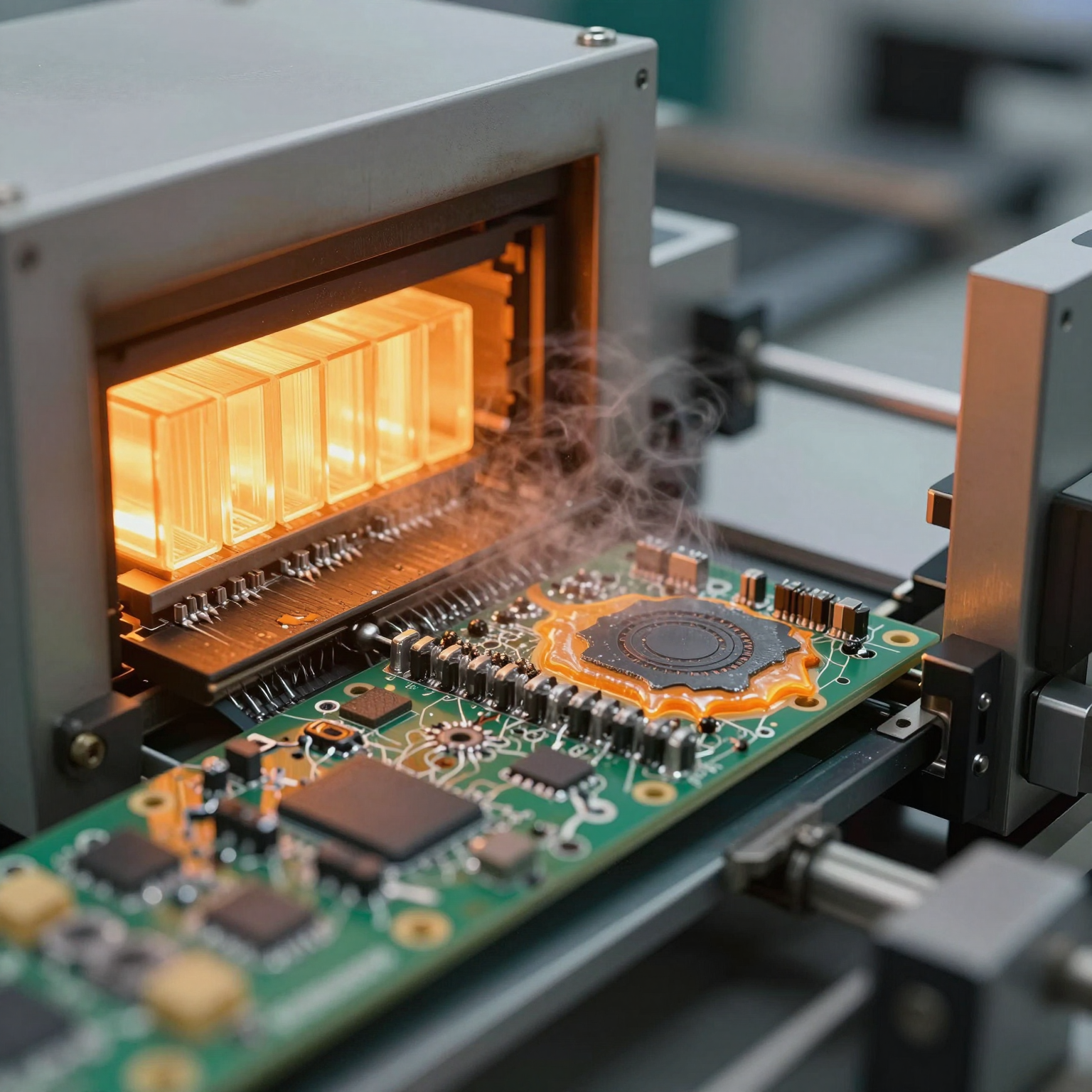
Once components are in place, the board passes through a reflow oven. Here, controlled heat melts the solder paste, forming permanent electrical and mechanical connections between the components and the board. After cooling, these joints solidify, securing the parts in place.
4. Through-Hole Component Insertion (if applicable)
Some designs require through-hole technology (THT), where component leads are inserted into drilled holes and soldered on the opposite side. This method is often used for larger or high-reliability components like transformers or heavy-duty connectors.
5. Wave Soldering or Manual Soldering
For through-hole components, wave soldering is commonly used. The board travels over a wave of molten solder, which wets the exposed leads and forms strong joints. In low-volume or prototype runs, manual soldering may also be employed.
6. Inspection and Testing
After assembly, each board undergoes visual inspection, automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray inspection (for hidden joints like BGA packages), and functional testing to ensure performance meets specifications.
Each of these steps contributes to the overall pcb assembly meaning, emphasizing precision, automation, and quality assurance throughout the manufacturing chain.
Surface Mount vs. Through-Hole
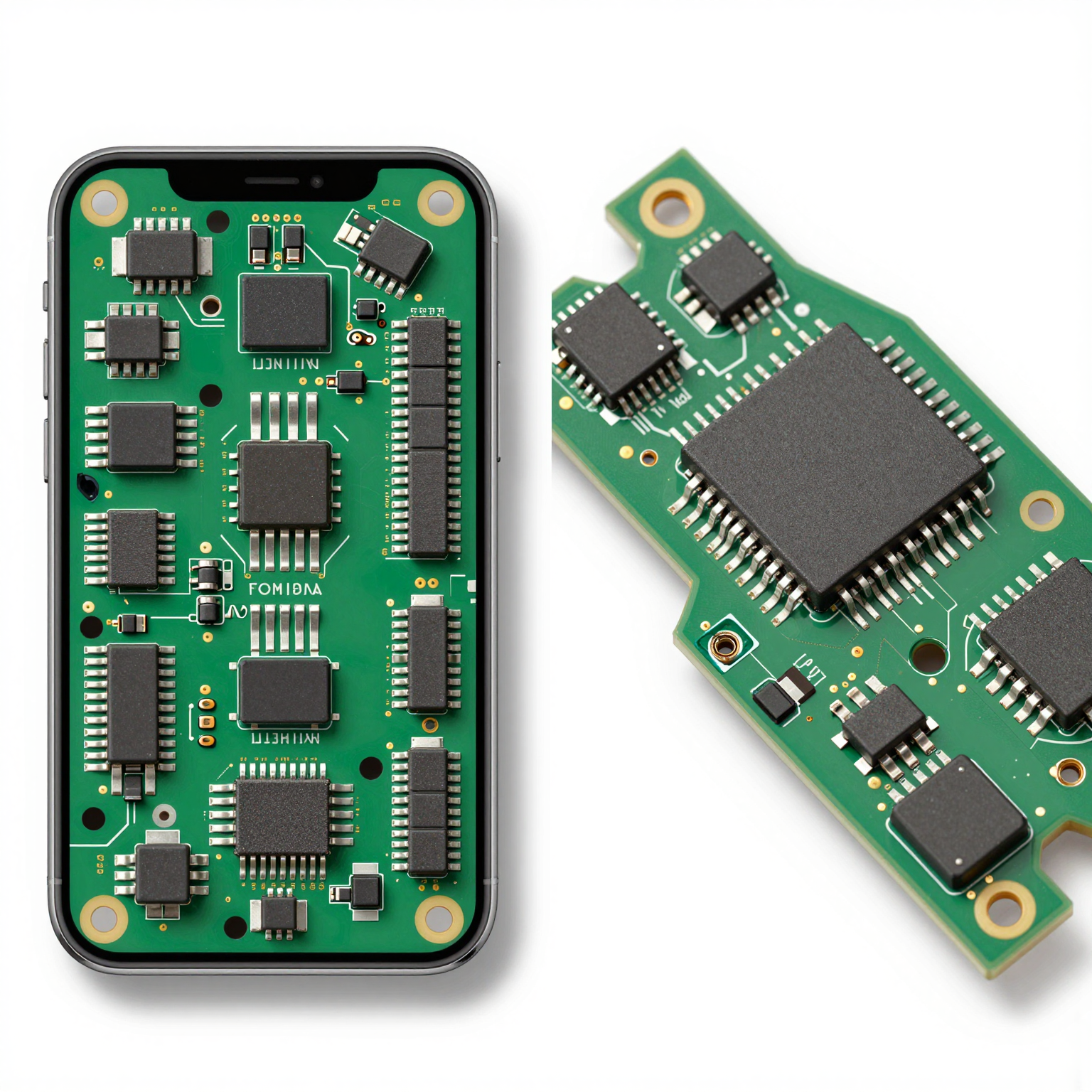
: Two Major Assembly Methods
One critical aspect of understanding pcb assembly meaning is recognizing the two primary techniques used in modern electronics: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT).
Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
SMT dominates modern PCB assembly due to its efficiency, miniaturization capabilities, and compatibility with automated production lines. Components are mounted directly onto the surface of the board without requiring holes. This allows for smaller footprints, higher component density, and faster assembly times.
SMT is ideal for mass-produced consumer electronics like smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. Its advantages include:
- Smaller component sizes
- Higher circuit speeds
- Lower production costs at scale
- Better performance under vibration
For more insights into these methods, check out our detailed comparison on SMT vs through-hole assembly.
Through-Hole Technology (THT)
While less common in consumer gadgets today, THT remains vital for applications requiring mechanical strength and durability. Components are inserted through pre-drilled holes and soldered on the backside, creating robust physical bonds.
THT is often found in:
- Industrial equipment
- Military and aerospace systems
- High-power electronics
- Prototyping environments
Though slower and more labor-intensive than SMT, THT offers superior reliability in harsh operating conditions.
Many modern PCBs use a hybrid approach, combining both SMT and THT components to leverage the strengths of each method—further enriching the pcb assembly meaning in complex electronic systems.
Why PCB Assembly Matters in Modern Electronics
The importance of pcb assembly meaning extends far beyond the factory floor. It plays a pivotal role in determining the functionality, reliability, and scalability of electronic products.
Enables Miniaturization and High Performance
Thanks to advanced PCB assembly techniques, manufacturers can pack immense computing power into tiny spaces. Devices like smartwatches and hearing aids rely on densely populated boards assembled with micron-level precision.
Supports Rapid Innovation Cycles
With automated assembly lines and streamlined workflows, companies can move quickly from design to prototype to mass production. Fast turnaround times enable rapid iteration, helping innovators stay competitive in fast-moving markets.
Ensures Consistency and Quality
Automated PCB assembly reduces human error and ensures uniformity across thousands—or even millions—of units. Combined with strict quality testing protocols, this leads to highly dependable end products.
Drives Cost Efficiency
Although initial setup costs for automated assembly can be high, the long-term savings in labor, material waste, and defect reduction make it economically viable for large-scale production.
These factors highlight why mastering the pcb assembly meaning is crucial for anyone involved in electronics design, procurement, or manufacturing.
Applications Across Industries
The relevance of pcb assembly meaning spans numerous sectors, each with unique requirements and challenges:
Consumer Electronics
Smartphones, TVs, gaming consoles, and home appliances all depend on efficient, high-speed PCB assembly to deliver affordable, feature-rich products.
Medical Devices
From MRI machines to portable glucose monitors, medical PCBAs must meet stringent safety and reliability standards. Cleanroom assembly and rigorous validation are standard practices.
Automotive Systems
Modern vehicles contain dozens of PCB assemblies controlling engine functions, infotainment, driver assistance systems, and electric vehicle battery management.
Industrial Automation
Robots, sensors, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) use ruggedized PCBs designed to withstand extreme temperatures, vibrations, and electromagnetic interference.
Aerospace and Defense
High-reliability assemblies with redundant circuits and specialized materials ensure mission-critical systems perform flawlessly under stress.
Each industry tailors the pcb assembly meaning to fit specific regulatory, environmental, and performance demands.
Choosing the Right PCB Assembly Partner
Understanding the pcb assembly meaning also involves knowing how to select a capable manufacturing partner. Whether you're developing a startup gadget or scaling up enterprise hardware, your choice of assembler impacts time-to-market, product quality, and total cost.
Key considerations include:
- Technical expertise in SMT, THT, and mixed-technology assembly
- Experience with your target industry (e.g., medical, automotive)
- Availability of value-added services like component sourcing and testing
- Compliance with international standards (e.g., IPC-A-610, ISO 9001)
- Scalability from prototypes to full-volume production
A trusted provider should offer transparent communication, design-for-manufacturability (DFM) feedback, and robust quality assurance processes.
For those seeking professional support, exploring comprehensive PCB assembly services can streamline development and improve outcomes.
If you’re ready to bring your next project to life, consider reaching out to a qualified team. You can learn more about our offerings by visiting our page on about PCB assembly company, or get started with a custom solution by contacting us directly to get a PCB quote.
Conclusion: Deepening Your Understanding of PCB Assembly Meaning
In summary, the pcb assembly meaning encompasses much more than simply putting parts on a board. It represents a convergence of engineering excellence, technological advancement, and meticulous craftsmanship that powers the digital age.
From the careful application of solder paste to the final functional test, every stage in the PCB assembly process contributes to the creation of intelligent, connected, and reliable electronic systems. As devices become smarter and more interconnected, the demand for precise, scalable, and innovative assembly solutions continues to grow.
Whether you're an engineer designing the next breakthrough gadget, a procurement manager sourcing components, or a student learning about electronics, understanding the pcb assembly meaning provides valuable insight into how modern technology comes to life.
By staying informed about best practices, emerging trends like HDI and flexible PCBs, and partnering with experienced manufacturers, businesses can ensure their products meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.
